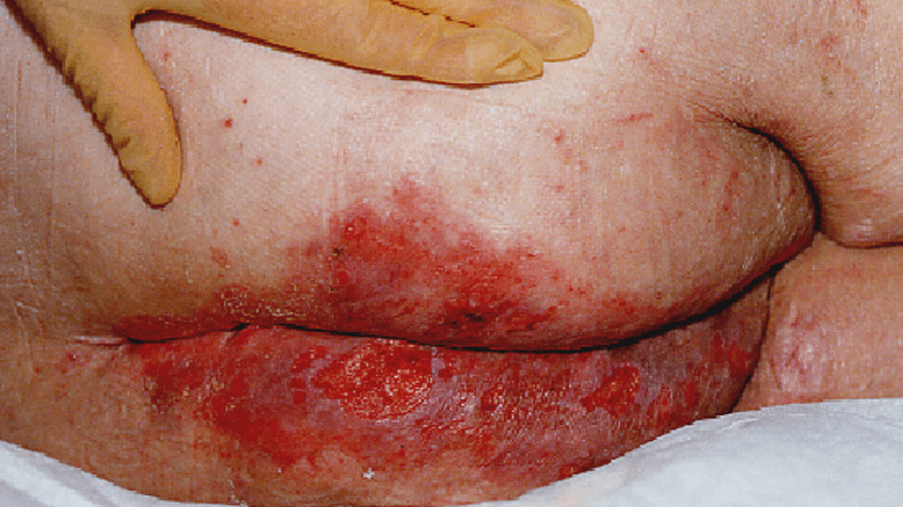
Incontinence associated dermatitis (IAD)
- Incontinence associated dermatitis appears as erythema (redness) and inflammation of the skin, sometimes with erosion or denudation (loss of the epidermis). (Dowsett, 2013)
- Ammonia from urine and enzymes from stool can disrupt the acid mantle of the skin and eventually cause the skin to break down.
- A systematic approach to the assessment of IAD, helps with early recognition of whether a patient is at increased risk of complications (Bianchi, 2012)
IAD
Once the barrier function of the skin is breached, it becomes far more likely to be attacked by bacteria, leading to the development of moisture lesions. The microorganisms strip away the epidermal layer, exposing the dermis and forming a lesion in the deeper layers of the skin.