Periwound and Peristomal Moisture Associated Dermatitis
Periwound moisture associated dermatitis
- Erythema (redness) and inflammation of the skin within approximately 4cm of the wound edge, sometimes accompanied by erosions or denudation (loss of the epidermis). (Dowsett, 2013)
- Excessive amounts of exudate can cause maceration and breakdown of periwound skin.
- Exudate from chronic wounds has been found to contain a higher concentration of proteolytic enzymes as compared to exudate from acute wounds. (Romanelli et al., 2010)
- Accurate wound and patient assessment must take place so that appropriate treatment can be planned.
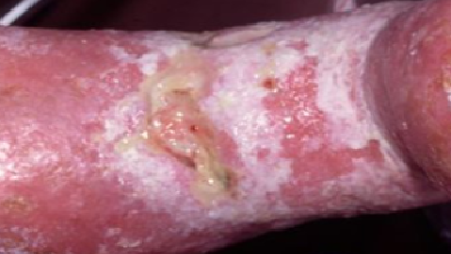
The skin surrounding a wound that is macerated is vulnerable and can easily break down, leading to a potential increase in wound size.
Peristomal moisture associated dermatitis
- Erythema (redness) and inflammation of the skin around the stoma, at times accompanied by denudation (loss of epidermis). (Dowsett, 2013)
- MASD that begins at the stoma/skin junction and can extend outwards in a 10cm radius. (Colwell et al., 2011)